- What are Flavouring substances?
- What chemicals are in artificial flavoring?
- What are some examples of Flavouring?
- Is natural flavor a chemical?
- What are the 5 flavors?
- What is Flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals?
- What are the 4 flavors?
- What are the 6 flavors?
- What are flavours and flavours?
- What are nature-identical flavoring substances?
What are Flavouring substances?
According to Codex Alimentarius “flavourings or flavouring substances are added to food to impart aroma or taste. Flavours are used as additives to enhance, modify the taste and the aroma in natural food products which could have got lost due to food processing.
What chemicals are in artificial flavoring?
In reality, we were smelling chemicals: methyl cyclopentenolone, diacetyl, methyl methoxy pyrazine, and benzaldehyde to be exact—four common ingredients found in both natural and artificial flavors.
What are examples of flavors?
We have receptors for five kinds of tastes:
- sweet.
- sour.
- salty.
- bitter.
- savory.
What are some examples of Flavouring?
The flavorings of commercially produced food products are typically created by flavorists….Flavorants or flavorings.
| Chemical | Odor |
|---|---|
| Diacetyl, acetylpropionyl, acetoin | Buttery |
| Isoamyl acetate | Banana |
| Benzaldehyde | Bitter almond, cherry |
| Cinnamaldehyde | Cinnamon |
Is natural flavor a chemical?
In the case of a natural flavor, the original source must be a plant or animal. By contrast, the original source of an artificial flavor is a synthetic chemical (5). Importantly, all flavors contain chemicals, whether they are natural or artificial.
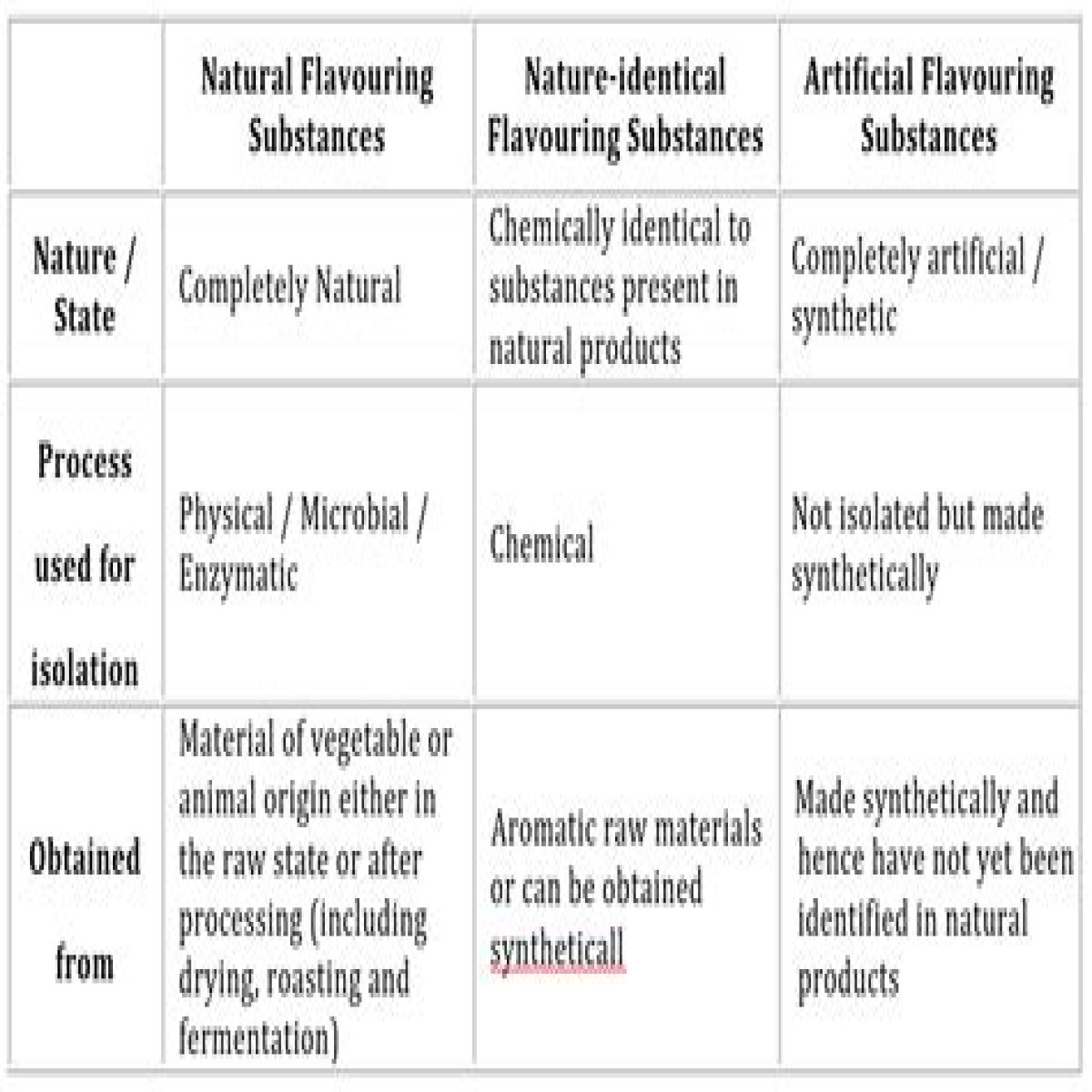
What are natural Flavouring substances?
Natural flavoring substances: These are substances that are obtained from plant or animal raw materials, by physical, microbiological or enzymatic processes.
- They can be either used in their natural form or processed form for consumption.
- Examples: spices, fruit juices, eggs, herbs, edible yeast, vegetable juice.
What are the 5 flavors?
5 basic tastes—sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami—are messages that tell us something about what we put into our mouth, so we can decide whether it should be eaten. Get to know about 5 basic tastes and learn why they matter to us.
What is Flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals?
Definition of Flavoring Agent According to USP, a flavoring agent is a single chemical entity or a blend of chemicals of synthetic or natural origin that can produce a taste or aroma (i.e. fragrance) when consumed orally or smelled. Flavoring agents are one of the excipients in some pharmaceutical formulations.
What is an organic flavor?
What about “organic” natural flavors? For “organic foods,” the natural flavor must have been produced without synthetic solvents, carriers and artificial preservatives. In “foods made with organic ingredients,” food processors have greater leeway to use synthetic extraction or carrier solvents.
What are the 4 flavors?
Western food research, for example, has long been dominated by the four “basic tastes” of sweet, bitter, sour and salty. In recent decades, however, molecular biology and other modern sciences have dashed this tidy paradigm. For example, Western science now recognizes the East’s umami (savory) as a basic taste.
What are the 6 flavors?
The six tastes are: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, pungent and astringent. They are present in substances. Each one produces more strength (for the body) than the one which follows it.
What are the substances used in flavoring?
The most often used substances include citral which tastes of lemon or menthol which gives a peppermint taste. Flavourings may contain flavouring substances, flavouring preparations, process flavourings, smoke flavourings and other flavourings.
What are flavours and flavours?
Flavours and flavouring substances should also be of appropriate food grade quality; and be prepared and handled in the same way as a food ingredient.” Flavours are used as additives to enhance, modify the taste and the aroma in natural food products which could have got lost due to food processing.
What are nature-identical flavoring substances?
Nature-identical flavoring substances: Nature-identical substances are the flavoring substances that are obtained by synthesis or are isolated through chemical processes in a lab but their chemical structures are identical to the substances present in natural products. These flavorings do not contain any artificial flavouring substances.
What is the Codex Alimentarius definition of flavour?
According to Codex Alimentarius “ flavourings or flavouring substances are added to food to impart aroma or taste. Like other food additives their use should not present an unacceptable risk to human health and should not mislead consumers.