- When was the last lobotomy performed in the US?
- What are lobotomies used for today?
- Did a lobotomy ever work?
- Why did lobotomies stop?
- Who has had a lobotomy?
- Who did lobotomies?
- Do lobotomies make you a vegetable?
- When did UK stop lobotomies?
- Did they do lobotomies in the UK?
- When were lobotomies last performed?
- Did they really use ice picks for lobotomies?
- Does a lobotomy erase memory?
- Is a chemical lobotomy permanent?
- What are the effects of Thorazine?
- Is Thorazine stronger than Seroquel?
- What is the safest antipsychotic drug?
- Why are antipsychotics bad?
- Do antipsychotics ruin your brain?
- Do antipsychotics shorten lifespan?
- Can you ever get off antipsychotics?
When was the last lobotomy performed in the US?
After 2,500 operations, Freeman performed his final ice-pick lobotomy on a housewife named Helen Mortenson in February 1967. She died of a brain hemorrhage, and Freeman’s career was finally over.
What are lobotomies used for today?
Today lobotomy is rarely performed; however, shock therapy and psychosurgery (the surgical removal of specific regions of the brain) occasionally are used to treat patients whose symptoms have resisted all other treatments.
What replaced lobotomy?
The transorbital lobotomy replaced the surgical lobotomy, shown here in a drawing from a 1951 textbook, Medical Psychology.
Did a lobotomy ever work?
Surprisingly, yes. The modern lobotomy originated in the 1930s, when doctors realized that by severing fiber tracts connected to the frontal lobe, they could help patients overcome certain psychiatric problems, such as intractable depression and anxiety.
Why did lobotomies stop?
In 1949, Egas Moniz won the Nobel Prize for inventing lobotomy, and the operation peaked in popularity around the same time. But from the mid-1950s, it rapidly fell out of favour, partly because of poor results and partly because of the introduction of the first wave of effective psychiatric drugs.
When did the lobotomy become illegal?
The Soviet Union banned the surgery in 1950, arguing that it was “contrary to the principles of humanity.” Other countries, including Germany and Japan, banned it, too, but lobotomies continued to be performed on a limited scale in the United States, Britain, Scandinavia and several western European countries well into …
Who has had a lobotomy?
Rosemary Kennedy, sister of President John F. Kennedy, underwent a lobotomy in 1941 that left her incapacitated and institutionalized for the rest of her life. Howard Dully wrote a memoir of his late-life discovery that he had been lobotomized in 1960 at age 12.
Who did lobotomies?
| Walter Jackson Freeman II | |
|---|---|
| Died | May 31, 1972 (aged 76) |
| Education | Yale University University of Pennsylvania Medical School |
| Occupation | physician, neurologist, psychosurgeon |
| Known for | Popularizing the lobotomy Invention of the transorbital lobotomy |
Is lobotomy banned in India?
1960-70: Lobotomies come under scrutiny by sociologists who consider it a tool for ‘psycho-civilising’ society. They were banned in Germany, Japan and the Soviet Union. Limited psychosurgery for extreme medical cases is still practised in the UK, Finland, India, Sweden, Belgium and Spain.
Do lobotomies make you a vegetable?
Of course, the lobotomy always had its critics. Doctors, as well as the families of patients, protested that the surgery did nothing more than turn people into vegetables.
When did UK stop lobotomies?
Decline of psychosurgery. The use of psychosurgery in the United Kingdom peaked in the late 1940s and early 1950s, with nearly 1,500 operations a year. Although some mental hospitals never used psychosurgery, or abandoned it after a brief trial, only a few voices were raised against it in the medical literature.
Are lobotomies banned in the UK?
In the UK this surgery is only used – as a last resort – in cases of severe depression or obsessive compulsive disorder. It’s likely Zavaroni fought hard to have the op. Unlike all other psychiatric treatments, lobotomies cannot be given without the consent of the patient in this country.
Did they do lobotomies in the UK?
More than 20,000 lobotomies were performed in the UK between the early 1940s and the late ’70s. They were typically carried out on patients with schizophrenia, severe depression or Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) – but also, in some cases, on people with learning difficulties or problems controlling aggression.
When were lobotomies last performed?
In 1967, Freeman performed his final lobotomy on a patient who died from a brain hemorrhage. He was never allowed to operate in another hospital again and died of cancer in 1972.
Who made lobotomies popular?
The doctor is Walter Freeman, pioneer of the infamous transorbital lobotomy, and the PBS documentary “The Lobotomist” tells the gruesome story of his rise and fall. Freeman, the laboratory director at a mental hospital, spent many late nights bent over the dissecting table at the morgue.
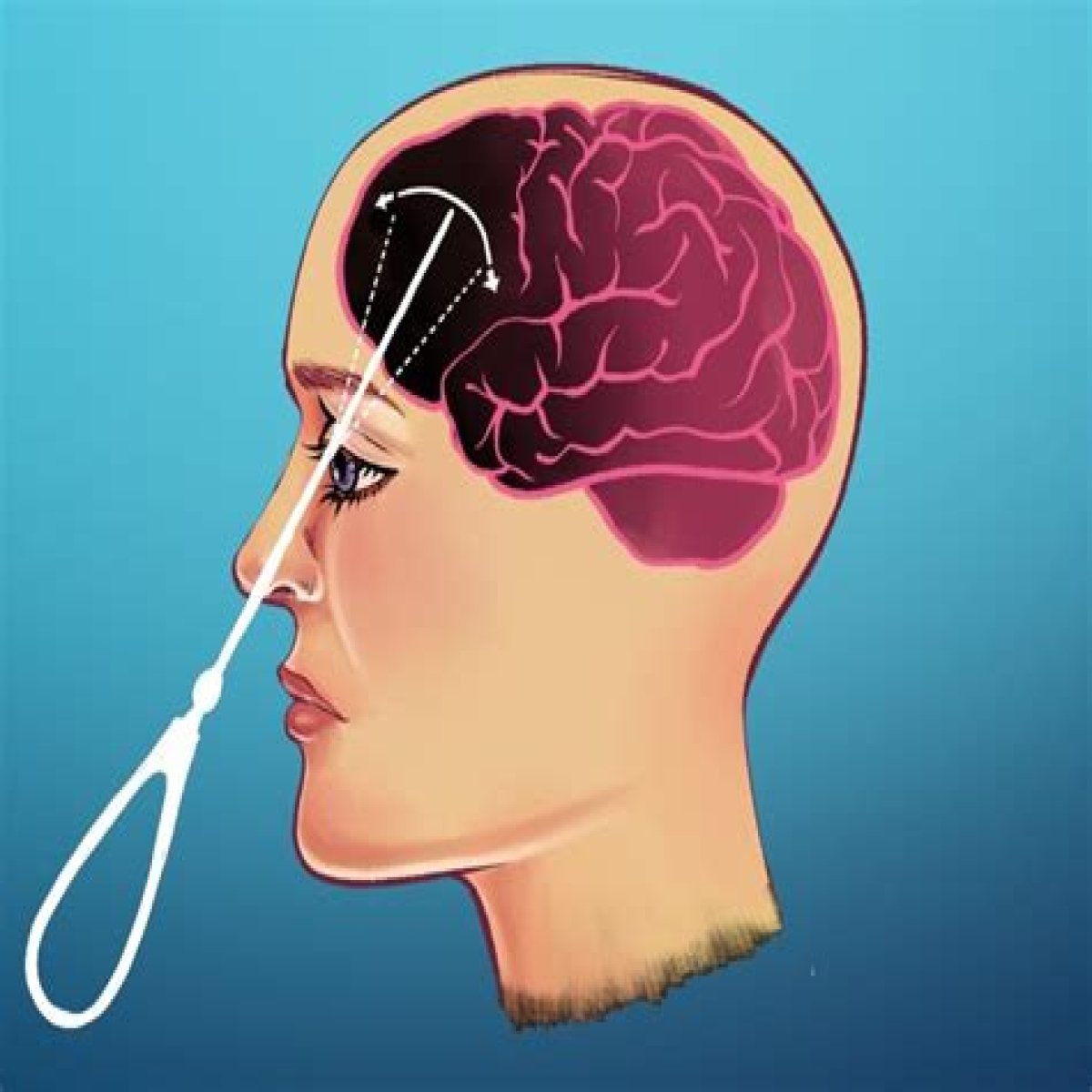
Did they really use ice picks for lobotomies?
He used a tool he’d found in his kitchen — an ice pick. Freeman realised he could easily reach the brain by using the icepick, which was into the brain through the eye sockets; he named this radically invasive form of brain surgery a “transorbital lobotomy” but it became more commonly known as the “icepick lobotomy”.
Does a lobotomy erase memory?
As if by erasing memory in the brain we can erase traumatic experience and make it as if nothing happened. All gone, all better. This amounts to a chemical lobotomy to erase memories. The lobotomy fantasy, even without a surgical ice pick, never seems to die.
What is someone like after a lobotomy?
Freeman believed that cutting certain nerves in the brain could eliminate excess emotion and stabilize a personality. Indeed, many people who received the transorbital lobotomy seemed to lose their ability to feel intense emotions, appearing childlike and less prone to worry.
Is a chemical lobotomy permanent?
If allowed to, it will play itself out, express itself and then naturally fade away—even if this takes several weeks or months.
What are the effects of Thorazine?
Drowsiness, dizziness, lightheadedness, dry mouth, blurred vision, tiredness, nausea, constipation, weight gain, or trouble sleeping may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Is there such a thing as a chemical lobotomy?
Furthermore, the use of antipsychotic drugs long has been referred to as a “chemical lobotomy” because they actually can disable normal brain function. Along with brain shrinkage, antipsychotics also can cause obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes.
Is Thorazine stronger than Seroquel?
Thorazine (chlorpromazine) has more side effects than other medicines like it. It is most useful during psychotic episodes because it slows you down quickly. Seroquel (quetiapine) is effective at relieving psychotic symptoms and manic episodes.
What is the safest antipsychotic drug?
Clozapine and olanzapine have the safest therapeutic effect, while the side effect of neutropenia must be controlled by 3 weekly blood controls. If schizophrenia has remitted and if patients show a good compliance, the adverse effects can be controlled.
What is the weakest antipsychotic?
Of the atypical antipsychotics, risperidone is the weakest in terms of atypicality criteria. Although early clinical studies with risperidone indicated that the incidence of EPS is not greater than that seen with placebo, this may not be the case.
Why are antipsychotics bad?
Some studies also raise the possibility that antipsychotic medication can cause structural changes in certain brain regions, leading some to raise the alarm about “brain damage” from these drugs.
Do antipsychotics ruin your brain?
Research on other kinds of structural brain changes caused by antipsychotic drugs has been negative to date. There is no evidence, for example, that antipsychotic drugs cause any loss of neurons or neurofibrillary tangles such as are found in Alzheimer’s disease.
Do antipsychotics make you emotionless?
Sedation, or sleepiness, is a common side effect of many antipsychotics. It is more common with certain antipsychotics than others, such as chlorpromazine and olanzapine. Sedation can happen during the day as well as at night. So if you experience this you might find it very hard to get up in the morning.
Do antipsychotics shorten lifespan?
An analysis of 11 studies examining physical morbidity and mortality in patients receiving antipsychotics showed a shorter life expectancy in the patients compared to others by 14.5 years. The researchers attributed this to growing life expectancy overall, plus a gap in healthcare received by schizophrenia patients.
Can you ever get off antipsychotics?
Some people may be able to stop taking antipsychotics without problems, but others can find it very difficult. If you have been taking them for some time, it can be more difficult to come off them. This is especially if you have been taking them for one year or longer.